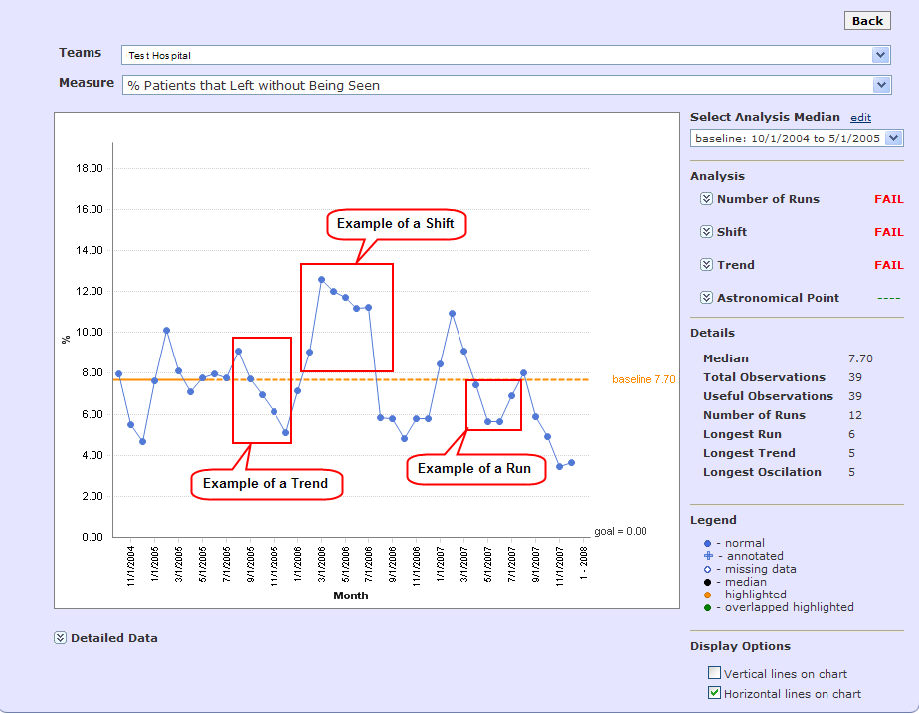
A run chart plots data over time with the time unit on the x-axis and the indicator on the y-axis. The run charts support multiple medians and run three simple statistical tests:
Number of runs&emdash; this test determines whether there are too few or too many runs in the data set. The number of runs is determined by comparing the total number of data points not on the median and compares them to a table containing the lower and upper limits for the number of runs. If the number of runs is above the upper limit or below the lower limit, it may signal a non-random pattern that should be investigated.
Shift&emdash; this test identifies a shift in the process. A run containing six or more data points all above or all below the median indicates a non-random pattern that should be investigated.
Trend&emdash; this test identifies a low-probability trend in the data set. A trend is defined as five or more consecutive points constantly increasing or constantly decreasing. If a trend is detected, it might indicate a non-random pattern that should be investigated.
The astronomical point is not an automated test but a way to identify a data point that is dramatically different from the rest of the data.
Run charts can be found from the Reports tab under the Advanced Reports heading.
